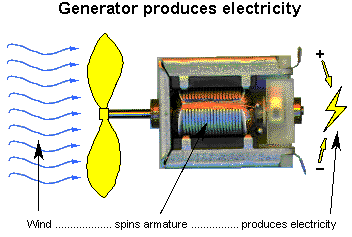
When the first thought came about building a renewable energy station, it was based on being able to run an electric space heater 24/7, not to power a whole house or neighborhood. The principles are the same though.
Many, if not most, space heaters are designed to work with normal wall sockets, which are mostly 20 amps. Maximum for one of these is about 2000 watts but you don’t want to get anywhere near that. At 1500 watts, the average space heater uses about 12-15 amps.
Lets start by looking at what generators, motors, and alternators are and some of the similarities and differences between them.
The motor and the generator are almost similar from the construction point of view, as both have stator and rotor. Electric motors and generators are differentiated by the function of the motor and generator, whether it consumes or produces electricity, its driven element, and the existence of the current in the winding. The main difference between them is in regard to what spins and what is fixed.
There is also a difference in size as alternators can fit into a small space, while generators are larger.
Generators and alternators are the primary methods of producing electric power. Generators create direct current (DC) power and alternators create alternating current (AC)

In terms of design, a DC generator is the simpler of the two. In fact, a DC generator can be used as a DC motor by applying power to the shaft, while the opposite is also true — turn the shaft of a DC motor, and it will act as a generator. This is one of the greatest benefits of a generator: It will produce power purely from mechanical motion. As long as you turn the shaft, the generator will produce electricity.
AC Alternator Design
AC alternators are more complex electrically because they must convert AC to DC and this takes extra circuitry. Theoretically, an alternator can act as an AC motor, but it will not be a very good motor. However, an alternator produces a large amount of electricity and typically provides enough electricity to power all the devices on a car without taxing the battery at all.
Power Generation
The generator is the exact opposite of the alternator. In the generator, a winding of wires spins inside a magnetic field to create a current. In an alternator, a magnetic field is spun inside a winding of wires. Efficiency is on the alternator’s side, as the wire winding is the biggest and heaviest part of both devices, so the alternator is spinning the lightest part. This means the alternator can work at a higher speed and produce more power at lower speeds.
| Generators and alternators are the primary methods of producing electric power. Generators create direct current (DC) power and alternators create alternating current (AC). | |||
| Generator | Motor | Alternator | |
| Function | A Motor converts Electrical energy into Mechanical Energy The generator is the exact opposite of the alternator. In the generator, a winding of wires spins inside a magnetic field to create a current. |
The Motor is an electric device which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Electricity is used in the motor. | An Alternator converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.In an alternator, a magnetic field is spun inside a winding of wires. Efficiency is on the alternator’s side, as the wire winding is the biggest and heaviest part of both devices, so the alternator is spinning the lightest part. This means the alternator can work at a higher speed and produce more power at lower speeds. |
| Complexity | In terms of design, a DC generator is the simpler of the two. In fact, a DC generator can be used as a DC motor by applying power to the shaft, while the opposite is also true — turn the shaft of a DC motor, and it will act as a generator. This is one of the greatest benefits of a generator: It will produce power purely from mechanical motion. As long as you turn the shaft, the generator will produce electricity. | Similar to a generator, as long as you turn the shaft, the motor will produce electricity. | In an alternator, electricity is produced when a magnetic field spins inside the stator (windings of wire). AC alternators are more complex electrically because they must convert AC to DC and this takes extra circuitry. Theoretically, an alternator can act as an AC motor, but it will not be a very good motor. However, an alternator produces a large amount of electricity and typically provides enough electricity to power all the devices on a car without taxing the battery at all. |
| Electricity | It generates electricity. | It uses electricity. | It generates electricity |
| Driven element | The Shaft is attached to the rotor and is driven by mechanical force. | The Shaft of the motor is driven by the magnetic force developed between armature and field. | The shaft is driven by mechanical force. |
| Current | In the generator current is produced in the armature winding. | In a motor the current is to be supplied to the armature winding. | In the alternator current is produced in the armature winding. |
| Classification | Generators are often comprised of special coils of wire that form what is referred to as the rotor. This rotor is positioned in the interior section of the magnetic field that is produced by the use of polarized magnets. | A motor is basically a generator. | The alternator is often classified as a generator. An alternator is a regarded as a special type of generator, which can be used to convert mechanical energy into electrical power that is often produced as alternating current. In most cases, the alternators often comprise of individual wires that are stationary and unique mechanical energy is used to move the magnet. As a result, the magnetic field passes through a conductor and an electrical current is produced. |
| Examples | An electric car or bike is an example of electric motor. | Energy in the form of electricity is generated at the power stations. | An auto alternator is best known. |
| Stepping Up or Down When you move beyond cars to commercial power generation, AC becomes the big winner. Transformers work only with AC. Because of this, a transformer can easily step up or step down the voltage from an alternator. When the voltage is stepped up, it is much easier to send it long distances over power lines with good efficiency, then step it down again for use in your home. |
|||
Stepping Up or Down
When you move beyond cars to commercial power generation, AC becomes the big winner. Transformers work only with AC. Because of this, a transformer can easily step up or step down the voltage from an alternator. When the voltage is stepped up, it is much easier to send it long distances over power lines with good efficiency, then step it down again for use in your home.
The other notable difference between these two components Is that the alternators and generators tend to differ when it comes to charging. To be specific, the alternator can not be used to charge a dead battery and lack of sufficient charge may lead to long term damage. On the contrary, the generator can be used to charge dead batteries as well.
Here are some motors/generators:
 These folks are measuring the rpms and power output using a motor driven setup. These folks are measuring the rpms and power output using a motor driven setup. |
 A good way to tell what the motor produces is to attach a hand drill or other motor to the main shaft and turn it with that. |
 There are even hand cranked generators. |
 Here an automobile alternator is used. They work too. |
 This one’s for sale – A 2000 watt generator weighing over a ton. |
 Of course, there’s this Cummins, complete with diesel. |
 For practical purposes we are dealing with generators more like this. |
 Or this. |
 This rig is running apparently without a controller. All it can do is charge the batteries. There is no metering. |
-
Summary:
- In an alternator, electricity is produced when a magnetic field spins inside the stator (windings of wire). On the other hand, the armature or the windings of wire in a generator spin inside a fixed magnetic field to generate electricity.
- Alternators conserve energy by using only the energy that is needed. Generators use all the energy that is produced.
- Alternators produce voltage when needed and generators produce voltage at all times.
- Alternators generate a higher output than generators.